D1.2 Roadmap of the research team in SDWM
1 Introduction
1.3 Positioning of the research group (UPB)
Achievements – short presentation of UPB papers
The UPB research group has technical and scientific achievements in coordination of research projects including EC funded projects (Data4Water, ERRIC, EU-NCIT, EGEE, SEE-GRID, Sensei, P2P-Next, etc.). The group has also experience in software development including the definition of software architectures, quality management processes, testing, and interoperability. The main research interests are: modelling and simulation, monitoring and control of large scale distributed systems, big data platforms, cyber-infrastructure and cyber-physical systems, vehicular ad-hoc networks, context-aware mobile wireless applications, solutions for natural resource management (water quality) using software platforms (deployed in Clouds), smart city architecture.
Using modern information technology, we proposed innovative solutions for water resource management, using the current state-of-the-art and situation of watershed science and management [Mocanu, 2013]. We concentrate our research on water pollution and we proposed a system for pollution detection, alert and pollution propagation simulation on the CyberWater (a national research project coordinated by our group) platform [Vacariu, 2015]. We designed decision support systems and decision makers during water pollution accidents [Salah, 2015], integrated decision support system for the evaluation of water pollution [Salah, 2014] and planning water quality management [Popescu, 2014]. The research was extended with decision support in risk related environments oriented on pollution events [Ciolofan, 2013], performances of monitoring water environments [Suciu, 2015] and prediction for water quality using bio-inspired methods [Pop, 2014].
Models are very important in the development of information systems for water management and they concern not only hydrology aspects, but also representations of complex software applications [Ionita, 2015a, 2015b]. We device an information-centric system for supporting decision-making [Mocanu, 2013], using advance techniques of modelling with SoaML [Ionita, 2013].
We investigate different approaches of integration of different Cloud computing platforms and services, in order achieve scalability, provisioning of resources in real time, to have a simplified deployment and management of resources and applications for river water quality [Negru, 2015]. And we proposed methods to support social‐based mobile networks [Pop, 2015a].
In environmental research the measurement, collection, storage, the same institution does not carry out the processing and analysis of data. So, there is a great complexity in environmental statistics motivated by the fact that heterogeneous data from different sources and collection principles are analysed simultaneously. To cope with this, we analysed different context-aware environments for the Internet of Things [Cristea, 2013] and identify the main requirements for data manipulation. There are dependencies between the measured quantities that usually do not follow fixed laws or rules, but reveal random variability. Besides this variability in the nature of the environmental problem there is variability of data in time and space. And measurements in time are not repeatable. So, behind huge volume of data, the research topics close to Big Data is motivated by data velocity and variety, and we made a comprehensive analysis on Big Data platforms for the Internet of Things [Ciobanu, 2014].
In the field of autonomous distributed systems, UPB group work more specifically in the optimization o task scheduling for many task computing [Sfrent, 2015], resource-aware management in heterogeneous distributed systems [Vasile, 2015], fault-tolerance of resource management in dependable distributed systems [Olteanu, 2012], evolutionary approach of scheduling and resource management [Pop, 2016], Big Data processing and distributed data aggregation services [Serbanescu, 2015], by complex simulation scenarios and real-world application and approaches. We proposed a new deadline scheduling for aperiodic tasks in inter-Cloud environments as a new approach to resource management [Pop, 2015b], [Pop, 2013]. We extended our research with directions on: GPU MapReduce framework for data intensive applications (Nitu, 2014), energy efficient cloud storage service [Negru, 2013], secure access to cloud resources [Musca, 2013] and a direction that is applied for any solution proposed, which is numerical optimization for smart data applications [Pop, 2014].
One focus of the distributed laboratory is towards research activities on applications of mobile and pervasive computing and sensing. The advent of new wireless sensor platforms in the hands of the masses (through recent miniaturization and subsequent introduction of sensors into commodity consumer electronics such as mobile phones, PDAs) makes possible a shift towards solving global-scale problems using public-sensing capabilities [Suciu, 2016]. Today we see a continuous push in this direction, and the advent of a new era of participatory (participatory sensing) or opportunistic (i.e. people-centric sensing) awareness. We embrace the holistic vision of massive quantities of real-time information becoming access push rather than demand pull on a global case (e.g., tweets, sensing info, GPS data). In this way we believe future enterprises will be (a) context aware, (b) dynamically configurable, and (c) multi-identity oriented virtual entities that manifest themselves in many different ways and re-invent themselves over and over again. Among results we mention: CAPIM is a context-aware platform designed to assist mobile applications make smarter assisted decisions (react to situation, contextually understand their environment); the SPRINT protocol is among the most advanced today social-based opportunistic networking routing protocol [Ciobanu, 2015] [Ciobanu, 2013], SENSE is a collaborative selfish node detection and incentive mechanism for mobile networks where collaboration among users is a most [Ciobanu, 2014], HYCCUPS is a contextual platform designed to assist smartphones take intelligent decisions to collaborate towards minimizing their energy footprint [Marin, 2014], and other solutions where we combined social aspects of mobile devices with context information towards advanced wireless networking aspects [Chilipirea, 2015].
Another focus of our laboratory is on Big Data and optimisation algorithms. As data volumes increase at exponential speed in more and more application fields of science, the challenges posed by handling Big Data in the Exabyte era gain an increasing importance. High-energy physics, statistics, climate modelling, cosmology, genetics or bio-informatics are just a few examples of fields where it becomes crucial to efficiently manipulate Big Data, which are typically shared at large scale. With the emergence of highly scalable infrastructures, e.g. for Cloud computing, multiple application classes that perform complex data processing (data mining, online transaction record management, etc.), initially reserved to governments and large corporations that could afford the underlying infrastructures to run them, now become accessible to a large public. In previous projects such as MonALISA or the Associate Team DataCloud@work collaboration between INRIA Rennes and UPB, the team obtained results on scalable data management in Cloud environments and self-adaptive behaviour of large-scale distributed systems based on monitoring information. We used evolutionary methods and models, like bio-inspired techniques for resources state prediction [Visan, 2011], a decomposition based algorithm for resource state prediction [Istin, 2010], and a pattern detection model [Dinu, 2011]. Using these techniques, we analysed the possibility to use them for resource management in an adaptive way.
On the top of middleware, we proposed a hybrid local-cloud framework for smart farms [Apostol, 2015], which represent an intelligent, integrated, cloud services-based system, using advanced computer technology, automation and communications to increase product quality and business development in the area of farming. We proposed solutions for real-time alerts [Raducu, 2015] and for time series analysis and visualization [Bojan, 2015].
Current research activities within the laboratory are focused on the research and development of solutions for managing large collections of data (e.g., in Smart City scenarios), collecting and aggregating context data, understanding and reasoning about context (through machine-learning techniques, semantic and temporal reasoning), the use of social awareness to deliver better sensing capabilities, and development of models for privacy, and data usage restrictions. Among particular applications of these solutions are: optimization of traffic, reduction of air-pollution in urban environments, the development of safety and non-safety applications to assist the drivers make informed decisions. The laboratory is, therefore, currently investigating issues at the intersection between the areas of Big Data, mobile and pervasive computing, context representation and reasoning, and privacy, with direct applications on creating the support for intelligent traffic systems, decision support system for water resource management.
Short presentation of UPB projects related to D4W
- CyberWater
Home page: http://cw.hpc.pub.ro/
Project Title: Prototype Cyberinfrastructure-based System for Decision-Making Support in Water Resources Management
Integrated and comprehensive approaches in decision-making processes associated with the management of water resources are necessary in acute problems, triggered by direct or indirect human interventions in the natural systems within which we live. Water resources management requires the processing of a huge amount of information with different levels of accessibility and availability and in various formats. Often, the data acquisition needs to be acquired, transmitted and accessed in real time. Equally important is to have access to historical data for calibration and validation of the models. With regard to the accessibility of stakeholders to information, there are situations when information is to be accessed only by designated stakeholders, but there is a huge amount of information that is, and should be handled, as public information.
The overarching goal of the CyberWater Project is to create an e-platform using advanced computational and communication technology for managing water and land resources in a sustainable and integrative manner, focused on pollution phenomena.
The progress of information and communication technologies makes possible the access to relevant information and to provide feedback on the observed processes by means of e-services and ancillary data repositories. The multi-agent approach encompasses agent types with various behaviour and specific interaction to the environment that are implemented as web-services. The proposed architecture of our prototype is presented below.
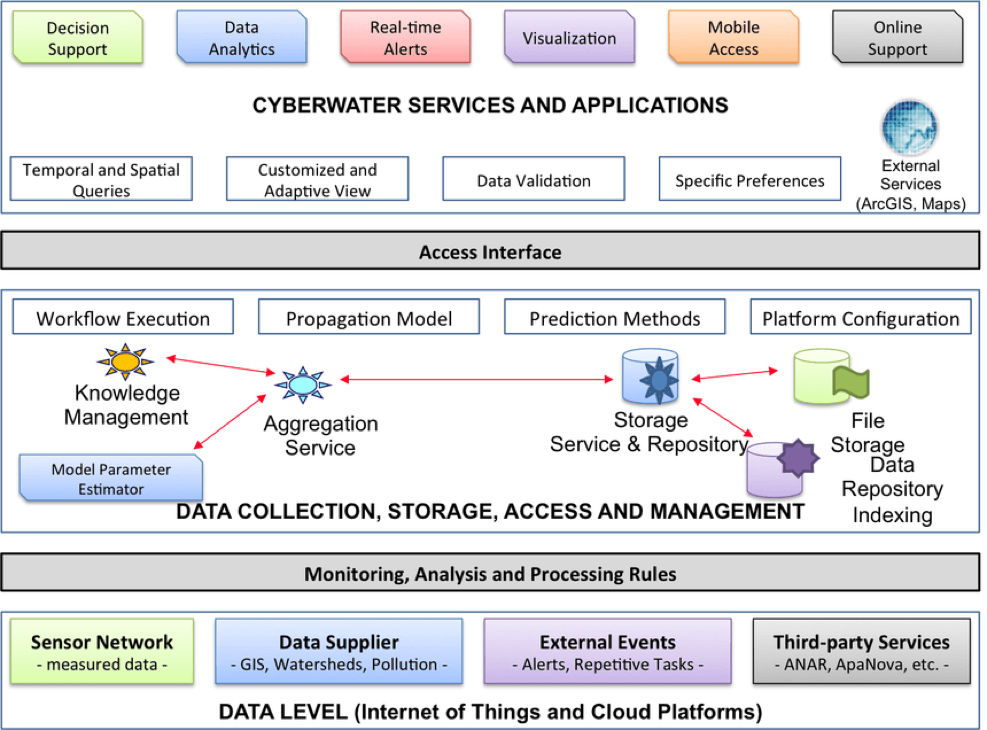
The specific objective is to implement a pilot platform for monitoring water pollution related phenomena and support to decision making in critical situation. Solving such water problems requires an interdisciplinary approach (hydrology, hydraulics, water quality, and ecosystem).
The composite application framework will integrate existing software and new e-services compliant to Directive 2007/2/EC regarding metadata for spatial data sets, data series and data services for environmental resources, protection and conservation.
- CLUeFARM
Home site: http://cluefarm.hpc.pub.ro
Project Title: Information system based on cloud services, accessible through mobile devices, for quality improvement of products and business development in farms
CLUeFARM is an Information system based on cloud services, accessible through mobile devices, for quality improvement of products and business development in farms.
The overall objective is to create an intelligent, integrated, cloud services-based system, using advanced computer technology, automation and communications to increase product quality and business development in the area of farming. The specific objective is to create an integrated control system for controlling the process in greenhouse crop production, using the services available on mobile devices. The services also offer simple and cheap integration of the existing infrastructure in various types of companies involved in agriculture. The added value generated by the system results from the creation of a virtual space that can be shared by several categories of companies.
The proposed solution is an intelligent system designed to increase the quality of the greenhouse grown products and to support the development of businesses in domains related to agriculture, based on cutting-edge IT&C technologies. Its components are: information infrastructure; the data acquisition subsystem; and subsystem for intervention in process (turning on/off water sources, adjusting temperature, etc.).
- DataCloud@Work
Home site: https://www.irisa.fr/kerdata/doku.php?id=cloud_at_work:start
Project Title: Associated team between KerData and Myriads teams from INRIA Rennes - Bretagne Atlantique and the Computer Science Department from Politehnica University of Bucharest.
DataCloud@Work is an associated team between KerData and Myriads teams from INRIA Rennes - Bretagne Atlantique and the Computer Science Department from Politehnica University of Bucharest. Our research topics address the area of distributed data management for cloud services. We investigated several open issues related to autonomic storage in the context of cloud services. The goal was to explore how to build an efficient, secure and reliable storage IaaS for data-intensive distributed applications running in cloud environments by enabling an autonomic behavior, while leveraging the advantages of the grid operating system approach.
- VANETS
Projects on Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks and Intelligent Transportation Systems
Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks (VANETs) are wireless ad-hoc networks formed among vehicles on the roads equipped with short range wireless communication devices. Such networks are particularly attractive because of their potential to improve comfort and safety of people in modern urban and highway situations. With the increase of the number of people depending on cars and road infrastructures, VANETs have the potential to optimise traffic conditions, and to reduce congestions and pollution. In University POLITEHNICA of Bucharest we conduct a number of research projects on VANETs. These projects are developed in joint collaboration with the Disco Lab Laboratory from Rutgers University, USA.
- MobiWay
Mobility Beyond Individualism: an Integrated Platform for Intelligent Transportation Systems of Tomorrow
MobiWay proposes the development of a collaborative platform designed to support ITS applications by acting as a middleware connection hub, offering an optimal support to different ITS partners and municipalities through and a data sharing and ITS support service integration platform. The goal is to develop a platform of ecosystems, to allow engaging communities in exploiting the shared value of mobility and collaborative cultures that can be leveraged beyond the classical views of social networks, respectively the current trends of service creation. The project sets out a new vision for using mobile computing capacities for provisioning and support of ubiquitous connectivity and real-time applications and services for smart cities’ needs.
- SideDOWN
Smart Internet Data Downloader and Aggregator
SideDOWN develops connectors for unstructured Web-based resources, and technologies to identify implicit Web entities and extracting information starting from such resources. The project extends the INTEMA platform with new business requirements, such as automatic collection of information, development of guided and profile-oriented search algorithms, personalised views.
- TRANSYS
Models and Techniques for Traffic Optimizing in Urban Environments
TRANSYS proposes the research and development of original models, methods and techniques for optimising traffic quality in urban environments. These solutions will target Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) and VANET networks. The main objective of this project is the research and development of models, methods and techniques to optimise traffic in urban environments. The project targets the Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS), the solutions being development within the VANET environments. This objective also assumes the development of solutions to reducing congestions in crowded traffic environments, the decrease of air-pollution and the adoption of solution to increase traffic safety capabilities. The derivate objectives complete the main objective with components and solutions defined within the project. The proposed models, methods and techniques will be based on a unitary set of solutions to ensuring security, optimised communication between vehicles and between vehicles and the road infrastructure and ensuring fault tolerance.
- MEDIOGRID
Parallel and distributed graphical processing on the grid structure of geographical and environment day
Industry development and social complexes have in recent decades led to dramatic changes of eco-systems. Level nuisances, pollution, atmospheric carbon dioxide generated atypical behavior of natural phenomena and weather - floods, fires, storms, downpours, droughts, strong winds - for our continent and in particular for Romania. Pursuing such critical events require a huge volume of observational data and high power computer processing in real time. The data come from observational and archived information from satellite images provided by geostationary satellites (e.g.. MSG-1 delivers 300 Mbps at an interval of 15 minutes). The project aims to create a system MEDIOGRID pilot imaging received in real time from weather satellites and resources, in order to extract meteorological and environmental parameters that characterise the state of the atmosphere and land surface. Applicability immediate project is the prognostication early evolution forest fires and floods. Satellite images acquired are preprocessed (decoding, quality checking, geometric correction and calibration), segmented by geographical areas and distributed grid infrastructure for parallel processing (noise masking and highlighting useful information). Images processed and reassembled to allow specialists initial geographic areas used in extracting information semantic interpretations and predictions immediate environmental phenomena studied. The project lasts 3 years. In the first year is done and experience the grid infrastructure and the initial data analysis and processing techniques. In the second year develops core software platform, consisting of basic components and algorithms for image segmentation and parallel processing and distributed data. Follow experimentation pilot processing system based on grid infrastructure. In the third year is developing and experimenting a pilot application specific analysis of social and ecological systems.
- DEPSYS
Models and Techniques for Ensuring Reliability, Safety, Availability and Security of Large Scale Distributed Systems
DEPSYS proposes a unified approach to all the aspects concerning dependable systems, by analysing and designing methods and techniques for improving reliability, availability, safety and security of large scale distributed systems. The main objective of this project is the research and development of models, methods and techniques for increasing reliability, availability, safety and security of large scale distributed systems. The research focus is on Grid systems, but the solutions developed will be applied to other types of systems, like those based on the Web.
- DataWay
Real-time Data Processing Platform for Smart Cities: Making sense of Big Data
More and more applications today use, generate and handle very large volumes of data. In particular, this is true for Smart City applications, which attract a rapidly increasing interest from government, companies, citizens, developers, scientists, etc. They cover a large spectrum of needs in public safety, water and energy management, smart buildings, government and agency administration, social programs, transportation, health, education. They are fed with huge amounts of input data, in various formats, from a continuously increasing number of sources (sensors, governmental, regional, and municipal sources, citizens, public open data sources, etc.), are describe by complex workflow and in many cases impose real-time processing capabilities, useful in decision taking. The DataWay project aims to develop Real-time Data Processing Platform for Smart Cities focusing on making sense of Big Data by extracting valuable information in an intelligent way by aggregation, reduction, retrieval, composition and decomposition of data processing tasks, which can de described by real-time analytics. The DataWay concept is as follow: Big Data is produced by Smart Cities Application and is processed and aggregated (top-down) and data extraction will make sense of Big Data (bottom-up).